Why DEX Aggregation Protocols for Institutions Are Defining the Next Competitive Frontier
In June 2025, a report by Messari revealed that over 38% of institutional DeFi trades now flow through DEX aggregation protocols like 1inch, CoW Swap, and OpenOcean. This figure is expected to rise as hedge funds and trading desks demand execution tools that mitigate slippage and unify fractured liquidity across dozens of chains.
Aggregation layers have become critical infrastructure in a multi-chain world where liquidity is increasingly fragmented. They do not replace exchanges—they sit on top, routing trades for best execution across them. As regulatory clarity grows and institutional volume deepens, these layers are no longer just DeFi-native tools—they’re enterprise trading middleware.
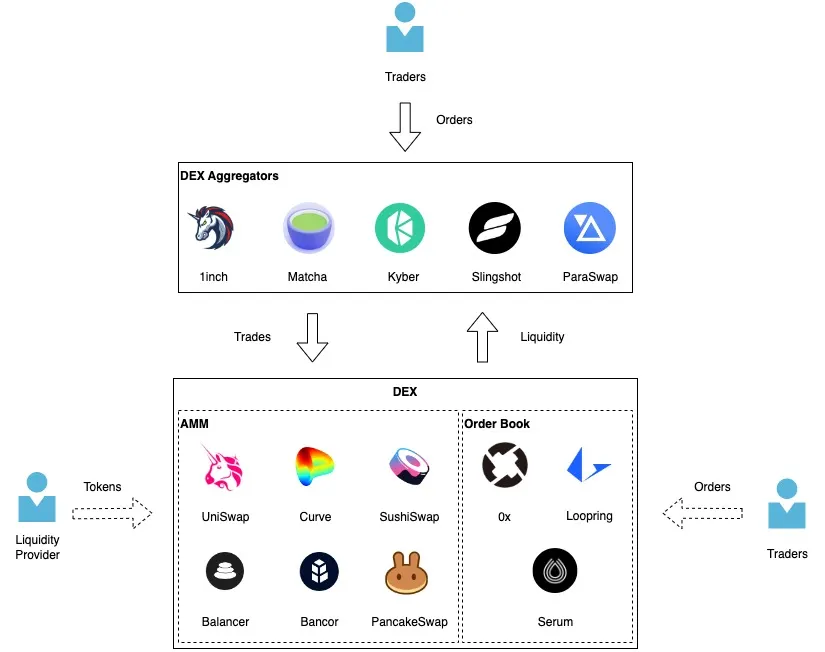
(Source: https://medium.com/@kaishinaw/dex-aggregators-an-introduction-to-liquidity-optimisation-ec14bd6afc1d)
DEX Aggregator Architecture Explained: How Aggregation Layers Work Under the Hood
Decentralized exchange (DEX) aggregators solve one of DeFi’s biggest challenges: fragmented liquidity. Unlike centralized exchanges where orders are matched on a single order book, DEX liquidity is scattered across hundreds of pools, chains, and protocols. An aggregation layer is the sophisticated backend infrastructure that stitches this liquidity together, ensuring traders get the best possible execution with minimal effort.
How Aggregation Layers Work: Core Components
At the heart of every efficient DEX aggregator lies a sophisticated aggregation layer – a complex system of interconnected components working in harmony to solve DeFi’s liquidity fragmentation problem. The trade routing engine serves as the central nervous system, constantly scanning and evaluating liquidity across multiple decentralized exchanges including Uniswap, Curve, and PancakeSwap. It doesn’t just look at surface-level prices but performs deep analysis of real-time liquidity conditions across various market types – from AMM pools to order-book DEXs and RFQ systems – while carefully weighing factors like pool depth, trading fees, and potential price impact before determining the optimal execution path.
Working in tandem with the routing engine, the Smart Order Router (SOR) acts as the strategic brain for large transactions. When faced with substantial trade sizes that could significantly move the market, the SOR employs advanced algorithms to intelligently split orders across multiple liquidity pools. Rather than simply chasing the best nominal rate from a single source, it pursues true price improvement by distributing execution across venues like Uniswap, Sushiswap and Balancer in proportions that collectively minimize overall slippage and market impact.
The multi-chain relayer expands this liquidity access even further by seamlessly bridging the gap between different blockchain ecosystems. By integrating with cross-chain communication protocols like LayerZero and Axelar, it enables asset movement between networks such as Ethereum, Arbitrum and Solana without requiring manual intervention from users. This component utilizes innovative techniques including meta-transactions and atomic swaps to maintain the trustless nature of decentralized trading while abstracting away the complexities of cross-chain operations.
Completing the system is the transaction bundler, which serves as both an efficiency booster and security safeguard. It optimizes gas usage by combining multiple operations – such as token approvals followed by swaps – into single atomic transactions. More importantly, it incorporates MEV protection mechanisms by potentially routing transactions through private mempools like Flashbots, shielding users from predatory front-running and sandwich attacks that plague naive DEX trading. Together, these components form an intelligent, multi-layered system that delivers professional-grade trade execution while maintaining the permissionless ethos of decentralized finance.
Why Aggregation Layers Matter
- Better Prices: By sourcing liquidity from multiple venues, traders avoid overpaying on illiquid pools.
- Lower Slippage: Large trades are split intelligently to reduce price impact.
- Cross-Chain Efficiency: Users don’t need to manually bridge assets—aggregators do it in the background.
- MEV Protection: Advanced routing minimizes sandwich attacks and other exploits.
Real-World Example: How a Trade Executes
When a trader initiates a swap—say, converting 100 ETH to USDC—the aggregator doesn’t just pick a single DEX. Instead, it scans multiple liquidity sources, including Uniswap, Curve, 1inch, and Balancer, comparing real-time rates, fees, and slippage across each. After analyzing the data, it determines the most cost-effective execution path—often splitting the trade into multiple chunks to minimize price impact. For example, it might route 50 ETH through Uniswap (deepest liquidity), 30 ETH through Curve (best stablecoin rates), and 20 ETH through a low-fee Balancer pool to optimize the overall return.
If liquidity on Ethereum is insufficient, the aggregator doesn’t stop there—it checks layer-2 networks like Arbitrum or Optimism, where ETH/USDC pools might offer better pricing due to lower fees or higher available volume. Once the optimal route is determined, the system bundles all necessary transactions—token approvals, swaps, and even cross-chain transfers—into a single, gas-efficient operation. This not only saves costs but also reduces exposure to MEV attacks.
Finally, the trader receives their USDC with maximum efficiency, getting the best possible rate without manually hopping between DEXs or worrying about liquidity fragmentation. The entire process happens in seconds, abstracting away the complexity while delivering institutional-grade execution to any user.
Key Benefits of Aggregation Layers for Institutional Crypto Traders
Before diving into architecture, it’s important to understand the business value aggregation layers unlock.
1. Unified Liquidity Across Fragmented Markets
With liquidity dispersed across hundreds of DEXs on multiple chains (Uniswap, SushiSwap, Balancer, Curve, etc.), executing large orders without aggregation leads to price impact and poor fills. Aggregation layers source the best pricing by scanning and routing across venues in real-time.
2. MEV Protection for Block Trades
Hedge funds placing large trades are often front-run by bots via miner extractable value (MEV). Sophisticated aggregators use techniques like time-weighted execution, dark order routing, and private relays to reduce this risk.
3. Faster Time-to-Market for Funds Launching in DeFi
Rather than integrate 50+ venues and chains directly, institutional desks can plug into a single API from an aggregator—saving engineering overhead and accelerating product deployment.
These aren’t theoretical benefits. In the last six months, firms using aggregation-powered DEX gateway have reported improved execution spreads, reduced failed transactions, and tighter compliance audit trails.
The Future of Institutional DeFi: Aggregation Layers as the Strategic Backbone
As hedge funds, trading firms, and market makers deepen their allocation into decentralized finance, the need for seamless liquidity access, optimized execution, and compliance-grade infrastructure becomes urgent. Fragmentation across blockchains and decentralized exchanges has made direct integration increasingly complex and inefficient.
Aggregation layers address this head-on by serving as the connective tissue between institutional capital and decentralized markets. They don’t just improve trading efficiency—they transform how institutions participate in DeFi. As hedge funds and liquidity providers deepen their participation in DeFi, the fragmentation challenge cannot be solved by a single DEX. Aggregation is no longer a convenience—it’s a requirement for scale.
Interested in building a Decentralized Exchange (DEX)? 📈
Contact ChainUp today to explore comprehensive crypto infrastructure solutions designed to empower your DeFi ventures. From white-label DEX software to Compliance-as-a-Service, ChainUp can help you launch and scale your decentralized trading platform.